无题
1 | title: Linux系统上常用软件集锦 |
[TOC]
卷积神经网络(CNN)花朵识别
一、前期工作
本文将采用CNN实现花朵识别
我的环境:
- 语言环境:Python3.6.5
- 编译器:jupyter notebook
- 深度学习环境:TensorFlow2
1. 设置GPU
如果使用的是CPU可以忽略这步
1 | import tensorflow as tf |
2. 下载数据
1 | import matplotlib.pyplot as plt |
3. 检查数据
数据集一共分为daisy、dandelion、roses、sunflowers、tulips五类,分别存放于flower_photo文件夹中的五个子文件夹中
1 | image_count = len(list(data_dir.glob('*/*.jpg'))) |
二、数据预处理
1. 加载数据
使用image_dataset_from_directory方法将磁盘中的数据加载到tf.data.Dataset中
1 | batch_size = 32 |
我们可以通过class_names输出数据集的标签。标签将按字母顺序对应于目录名称。
1 | class_names = train_ds.class_names |
2. 可视化数据
1 | plt.figure(figsize=(20, 10)) |

3. 再次检查数据
1 | for image_batch, labels_batch in train_ds: |
Image_batch是形状的张量(32,180,180,3)。这是一批形状180x180x3的32张图片(最后一维指的是彩色通道RGB)。Label_batch是形状(32,)的张量,这些标签对应32张图片
4. 配置数据集
- shuffle():打乱数据,关于此函数的详细介绍可以参考:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/42417456
- prefetch():预取数据,加速运行
prefetch()功能详细介绍:CPU 正在准备数据时,加速器处于空闲状态。相反,当加速器正在训练模型时,CPU 处于空闲状态。因此,训练所用的时间是 CPU 预处理时间和加速器训练时间的总和。prefetch()将训练步骤的预处理和模型执行过程重叠到一起。当加速器正在执行第 N 个训练步时,CPU 正在准备第 N+1 步的数据。这样做不仅可以最大限度地缩短训练的单步用时(而不是总用时),而且可以缩短提取和转换数据所需的时间。如果不使用prefetch(),CPU 和 GPU/TPU 在大部分时间都处于空闲状态:
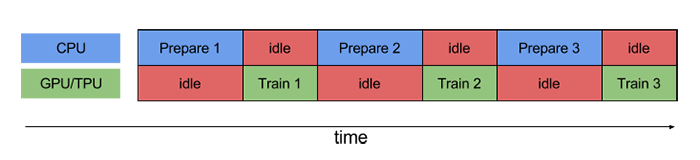
使用prefetch()可显著减少空闲时间:
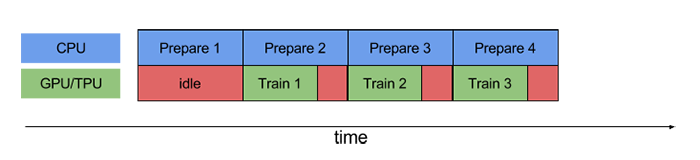
- cache():将数据集缓存到内存当中,加速运行
1 | AUTOTUNE = tf.data.AUTOTUNE |
三、构建CNN网络
卷积神经网络(CNN)的输入是张量 (Tensor) 形式的 (image_height, image_width, color_channels),包含了图像高度、宽度及颜色信息。不需要输入batch size。color_channels 为 (R,G,B) 分别对应 RGB 的三个颜色通道(color channel)。在此示例中,我们的 CNN 输入,fashion_mnist 数据集中的图片,形状是 (28, 28, 1)即灰度图像。我们需要在声明第一层时将形状赋值给参数input_shape。
1 | num_classes = 5 |
四、编译
在准备对模型进行训练之前,还需要再对其进行一些设置。以下内容是在模型的编译步骤中添加的:
- 损失函数(loss):用于测量模型在训练期间的准确率。
- 优化器(optimizer):决定模型如何根据其看到的数据和自身的损失函数进行更新。
- 指标(metrics):用于监控训练和测试步骤。以下示例使用了准确率,即被正确分类的图像的比率。
1 | model.compile(optimizer='adam', |
五、训练模型
1 | history = model.fit( |
六、模型评估
1 | plt.plot(history.history['accuracy'], label='accuracy') |
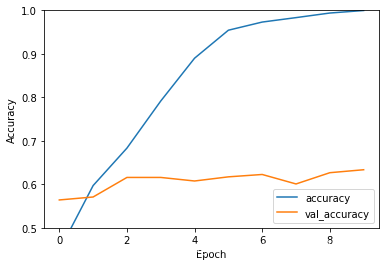
1 | 23/23 - 0s - loss: 2.1597 - accuracy: 0.6335 |
从上面可以看出随着迭代次数的增加,训练准确率与验证准确率之间的差距逐步增加,这是由于过拟合导致,解决办法请参考我的下一篇文章
1 | print("验证准确率为:",test_acc) |


